
DIAGNOSING ATTR‑CM1,2
Establish a
diagnosis in 3 steps*:
Follow the diagnostic algorithm for ATTR‑CM2,3†
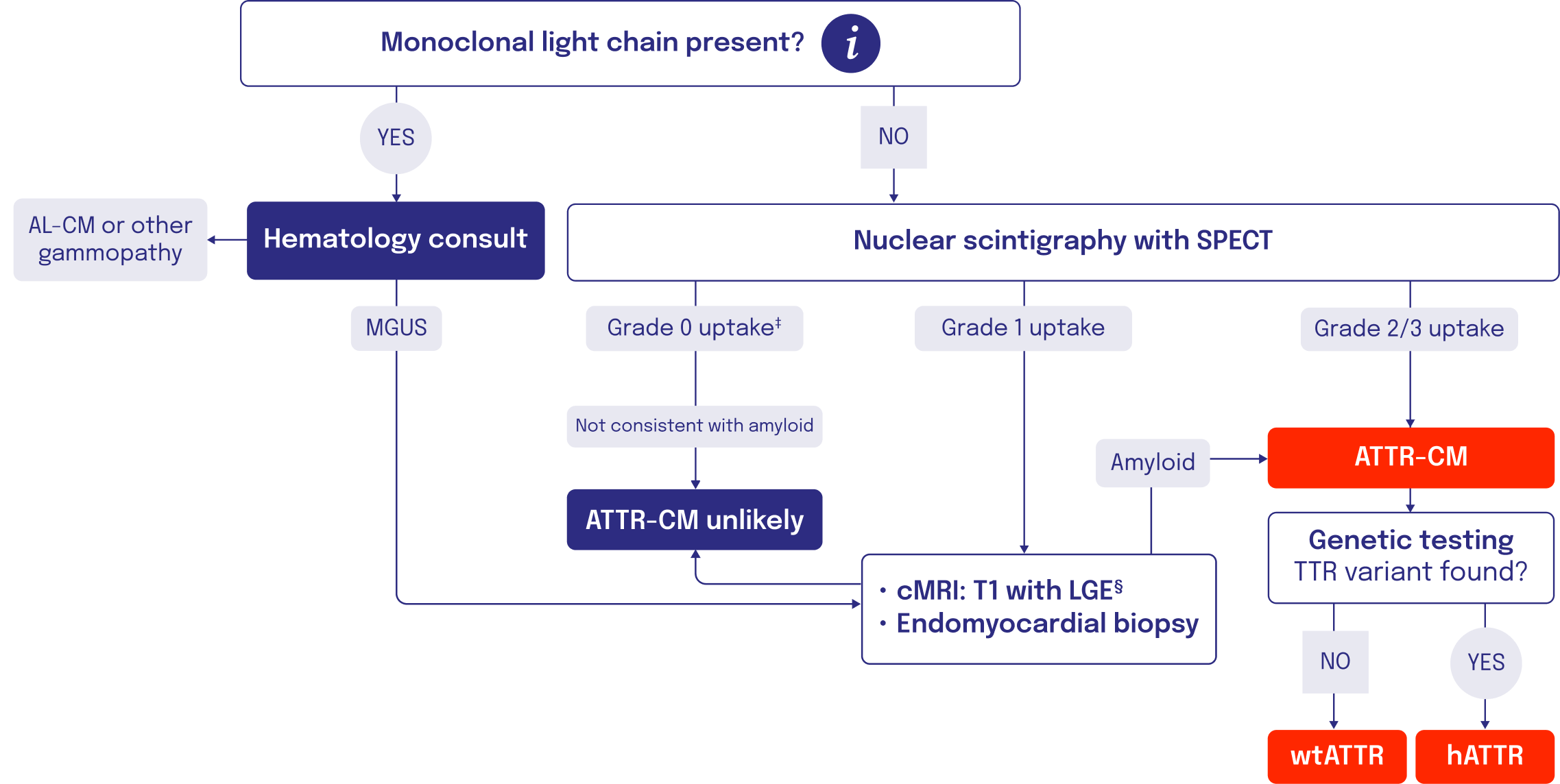
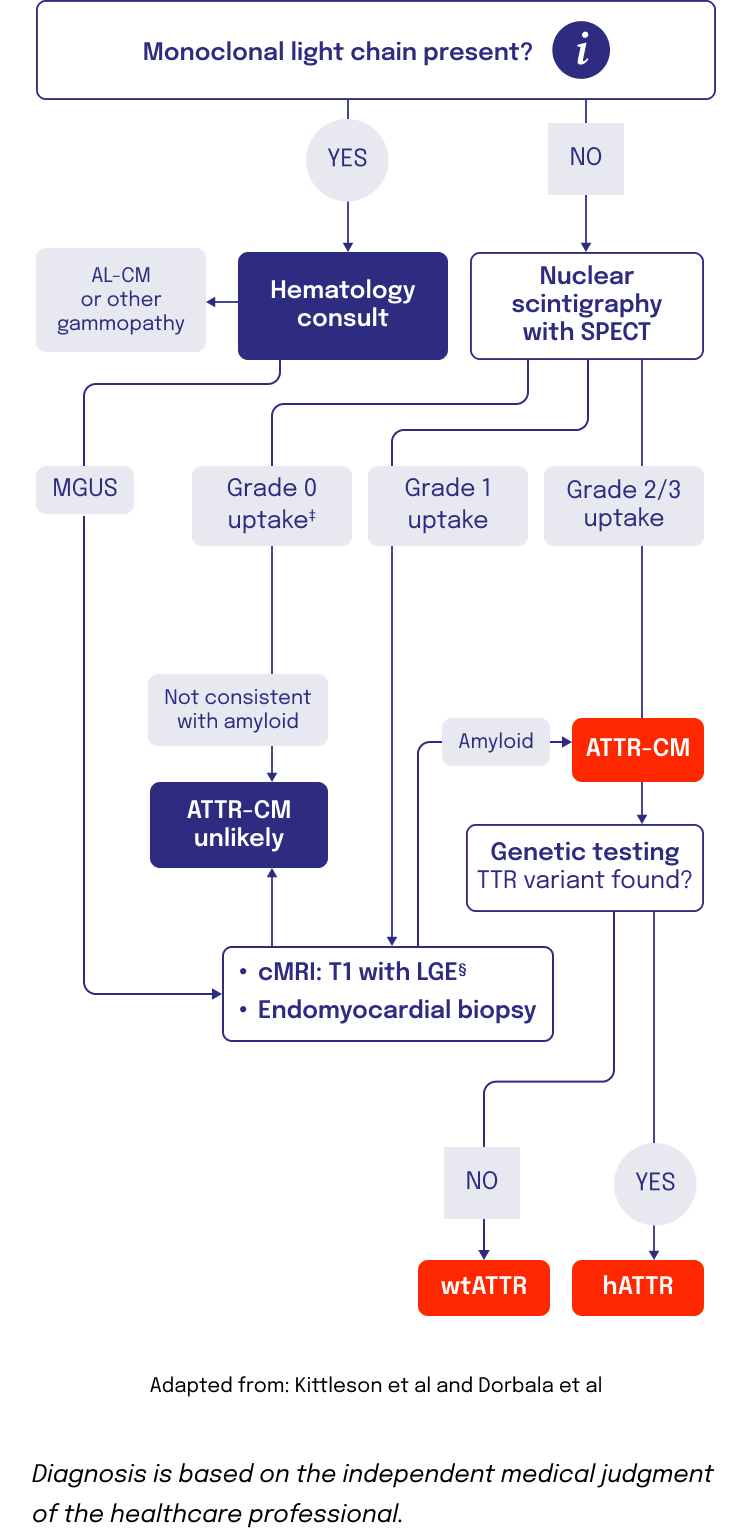
Imaging and other assessments can be used to confirm an ATTR-CM diagnosis
Nuclear scintigraphy5
- Scintigraphy is a noninvasive diagnostic that identifies amyloid buildup in the heart using radioactive tracers that bind to amyloid deposits6-8
- Radiotracers like 99mTc-PYP, 99mTc-DPD, and 99mTc-HMDP all have use within ATTR9
- SPECT or SPECT/CT imaging, in addition to planar imaging, is recommended for confirmation that uptake is in the myocardium, and not a result of blood pool radiotracer uptake3
- Scintigraphy with Grade 2/3 uptake confirms an ATTR-CM diagnosis. If the scintigraphy returns a score of Grade 0/1, but high suspicion of ATTR-CM remains, a tissue biopsy should be performed6
TISSUE BIOPSY2,4,10,11
- Biopsy of cardiac tissue with Congo red staining can detect TTR amyloid deposition
- Tissue biopsy is used when bone scintigraphy is negative despite a high clinical suspicion of ATTR-CM or if scintigraphy is unavailable
GENETIC TESTING1,2,12
- Genetic testing is a noninvasive process to detect TTR variants that will distinguish hATTR from wtATTR
- Alnylam Act®—Genetic Testing and Counseling Program
- Alnylam Act® offers third-party genetic screening and counseling programs for patients who may have hATTR amyloidosis at no charge to patients, physicians, and payers.
- Alnylam Act® is available for patients 18 years and older who may be at risk for carrying a genetic variant known to be associated with hATTR amyloidosis.
- The Alnylam Act® program was created to provide access to genetic testing and counseling to patients as a way to help people make more informed decisions about their health.
- While Alnylam provides financial support for this program, tests and services are performed by independent third parties. Healthcare professionals must confirm that patients meet certain criteria to use the program.
- No patients, healthcare professionals, or payers, including government payers, are billed for this program.
- Alnylam receives de-identified patient data from this program, but at no time does Alnylam receive patient-identifiable information. Alnylam uses healthcare professional contact information for research and commercial purposes.
- Healthcare professionals or patients who use this program have no obligation to recommend, purchase, order, prescribe, promote, administer, use, or support any Alnylam product.
Not a comprehensive list of all diagnostic tools.
*Refer to American Heart Association diagnosis guidelines on amyloidosis and heart failure for further details.
†Diagnosis is based on the independent medical judgment of the healthcare professional. Refer to American College of Cardiology expert consensus on cardiac amyloidosis for additional guidance. This algorithm has been developed based on the references cited as well as the collective expert consensus of key opinion leaders.
‡Some variants of hATTR are associated with grade 0 99mTc-PYP uptake in patients.3
§This step is relevant if not already conducted earlier in patient diagnostic journey to raise clinical suspicion.
99mTc-DPD=technetium-99m-3,3-diphosphono-1,2-propanodicarboxylic acid; 99mTc-HMDP=technetium-99m-hydroxymethylene diphosphonate; 99mTc-PYP=technetium-99m-pyrophosphate; AL=amyloid light chain; ATTR=transthyretin-mediated amyloidosis; ATTR‑CM=cardiomyopathy of transthyretin-mediated amyloidosis; CM=cardiomyopathy; CT=computed tomography; cMRI=cardiac magnetic resonance imaging; FLC=free light chain; hATTR=hereditary transthyretin-mediated amyloidosis; H/CL=heart-to-contralateral lung ratio; LGE=late gadolinium enhancement; MGUS=monoclonal gammopathy of uncertain significance; SPECT=single-photon emission computed tomography; TTR=transthyretin; wtATTR=wild-type transthyretin-mediated amyloidosis; wtATTR-CM=cardiomyopathy of wild-type transthyretin-mediated amyloidosis.
References:
- Kittleson MM et al. Circulation. 2020;142(1):e7-e22.
- Kittleson MM et al. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2023;81(11):1076-1126.
- Dorbala S et al. Circ Cardiovasc Imaging. 2021;14(7):e000029.
- Witteles RM et al. JACC Heart Fail. 2019 Aug;7(8):709-716.
- Hanna M et al. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020;75(22):2851-2862.
- Gillmore JD et al. Circulation. 2016;133(24):2404-2412.
- Ruberg FL et al. Circulation. 2012;126(10):1286-1300.
- Dharmarajan K et al. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2012;60(4):765-774.
- Gertz MA et al. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2015;66(21):2451-2466.
- Maurer MS et al. Circ Heart Fail. 2019;12(9):e006075.
- Gonzalez-Lopez E et al. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2024;83(11):1085-1099.
- Ando Y et al. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2013;8:31.


