Multiple approved therapeutic options exist for
patients with ATTR‑CM and hATTR‑PN
TTR silencers3,4
- Antisense oligonucleotides (ASOs) are short, chemically modified oligonucleotides that reduce the production of TTR protein
- RNA interference (RNAi) therapeutics are double-stranded small interfering RNAs (siRNAs) that reduce the production of TTR protein
TTR stabilizers2,3
- TTR tetramer stabilizers are drug molecules that bind to the TTR protein, preventing the dissociation into monomers
| Silencers | Stabilizers | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| FDA-approved to treat | RNAis | ASOs | Tetramer stabilizer |
| wtATTR-CM | |||
| hATTR-CM | |||
| hATTR-PN | |||
Early intervention after diagnosis is key to optimizing clinical outcomes.1,2
Mechanisms to target TTR1-3
TTR silencing works upstream of tetramer formation by suppressing TTR production at its source in the liver.1-3
TTR stabilizing works by reducing TTR dissociation and misfolding.1-3
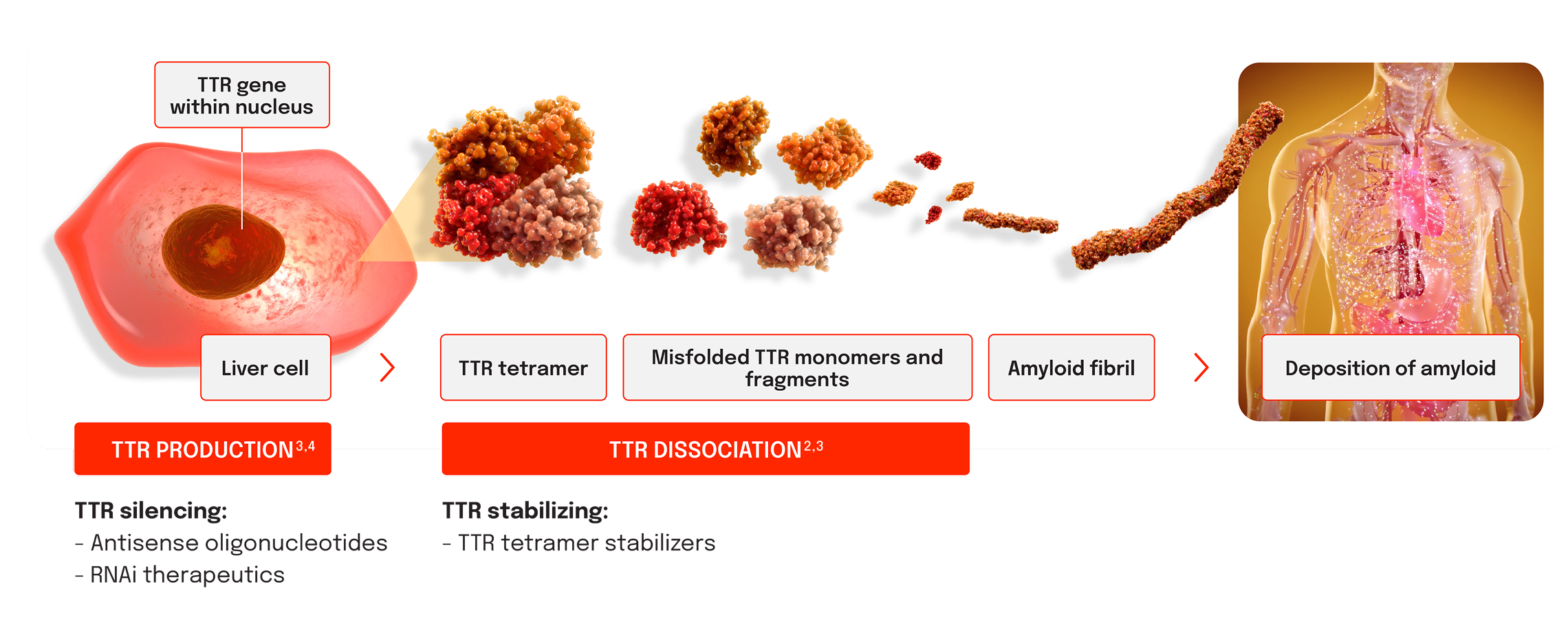
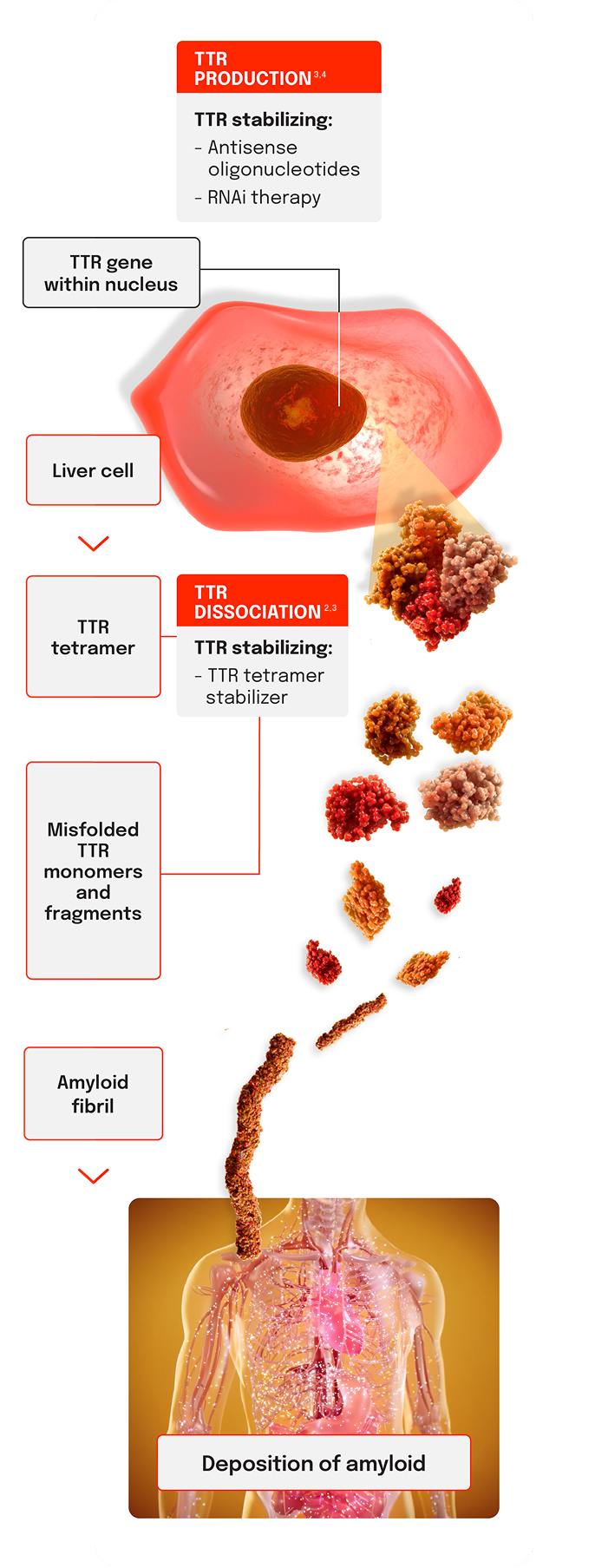
Liver cell image was AI generated.
ATTR=transthyretin-mediated amyloidosis; ATTR‑CM=cardiomyopathy of transthyretin-mediated amyloidosis; hATTR=hereditary transthyretin-mediated amyloidosis; hATTR-CM=cardiomyopathy of transthyretin-mediated amyloidosis; hATTR-PN=polyneuropathy of transthyretin-mediated amyloidosis; TTR=transthyretin; wtATTR=wild-type transthyretin-mediated amyloidosis.
References:
- Kittleson MM, et al. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2023;81(11):1076-1126.
- Kittleson MM, et al. Circulation. 2020;142(1):e7-e22.
- Sekijima Y. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2015;86(9):1036-1043.
- Brannagan TH, et al. J Peripher Nerv Syst. 2022;27(4):228-237.